- Linux Mac For Vlan Settings
- Linux Mac For Vlan Configuration
- Linux Mac For Vlan Command
- Macvlan Linux
- Linux Mac Based Vlan

Estimated reading time: 3 minutes
2 days ago VRRP is not supported on a VLAN interface with a user-configured MAC address. Linux, FreeBSD, Mac OS X¶ The dd command is the easiest way to erase the partition table from the USB memstick on UNIX and UNIX-like operating systems such as Linux, FreeBSD, and OS X. Advance skill on Switching (VLAN, VTP, Spanning Tree, RSTP, MST). The VLAN-aware mode in Cumulus Linux implements a configuration model for large-scale layer 2 environments, with one single instance of spanning tree protocol. Each physical bridge member port is configured with the list of allowed VLANs as well as its port VLAN ID, either primary VLAN Identifier (PVID) or native VLAN. MAC address learning.

Some applications, especially legacy applications or applications which monitornetwork traffic, expect to be directly connected to the physical network. Inthis type of situation, you can use the macvlan network driver to assign a MACaddress to each container’s virtual network interface, making it appear to bea physical network interface directly connected to the physical network. In thiscase, you need to designate a physical interface on your Docker host to use forthe macvlan, as well as the subnet and gateway of the macvlan. You can evenisolate your macvlan networks using different physical network interfaces.Keep the following things in mind:
It is very easy to unintentionally damage your network due to IP addressexhaustion or to “VLAN spread”, which is a situation in which you have aninappropriately large number of unique MAC addresses in your network.
Your networking equipment needs to be able to handle “promiscuous mode”,where one physical interface can be assigned multiple MAC addresses.
If your application can work using a bridge (on a single Docker host) oroverlay (to communicate across multiple Docker hosts), these solutions may bebetter in the long term.
Create a macvlan network
When you create a macvlan network, it can either be in bridge mode or 802.1qtrunk bridge mode.
In bridge mode,
macvlantraffic goes through a physical device on the host.In 802.1q trunk bridge mode, traffic goes through an 802.1q sub-interfacewhich Docker creates on the fly. This allows you to control routing andfiltering at a more granular level.
Bridge mode
To create a macvlan network which bridges with a given physical networkinterface, use --driver macvlan with the docker network create command. Youalso need to specify the parent, which is the interface the traffic willphysically go through on the Docker host.
If you need to exclude IP addresses from being used in the macvlan network, suchas when a given IP address is already in use, use --aux-addresses:
802.1q trunk bridge mode
Linux Mac For Vlan Settings
If you specify a parent interface name with a dot included, such as eth0.50,Docker interprets that as a sub-interface of eth0 and creates the sub-interfaceautomatically.
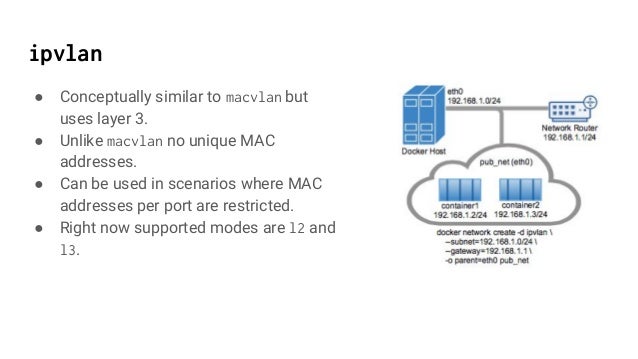
Use an ipvlan instead of macvlan
In the above example, you are still using a L3 bridge. You can use ipvlaninstead, and get an L2 bridge. Specify -o ipvlan_mode=l2.
Use IPv6

If you have configured the Docker daemon to allow IPv6,you can use dual-stack IPv4/IPv6 macvlan networks.
Linux Mac For Vlan Configuration
Next steps
Linux Mac For Vlan Command
Macvlan Linux
- Go through the macvlan networking tutorial
- Learn about networking from the container’s point of view
- Learn about bridge networks
- Learn about overlay networks
- Learn about host networking
- Learn about Macvlan networks
Linux Mac Based Vlan
network, macvlan, standalone